Understanding Jaundice Symptoms in Adults: A Comprehensive Guide
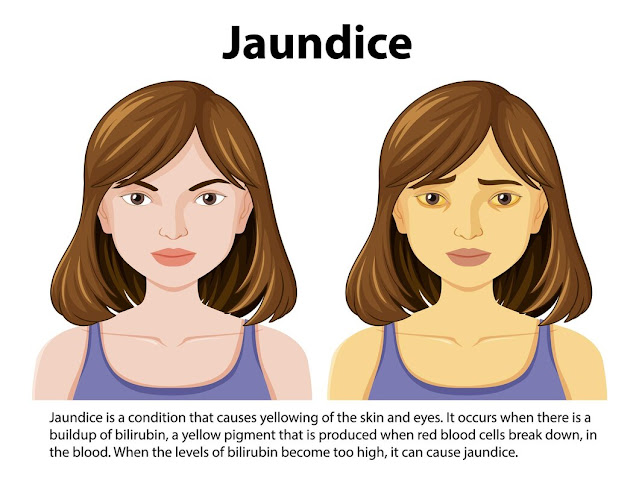
Jaundice is
a medical condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin, eyes, and
mucous membranes due to the accumulation of bilirubin in the body. It is not a
disease in itself but rather a symptom of an underlying issue affecting the
liver, gallbladder, or pancreas. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore
the various aspects of jaundice symptoms in adults, shedding light on the
causes, risk factors, and potential treatments.
This article aims to enhance awareness and
understanding of jaundice, empowering individuals to recognize the signs and
seek timely medical attention.
Understanding
Jaundice
Jaundice
occurs when there is an excess buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced
during the breakdown of red blood cells. Typically, the liver processes
bilirubin and excretes it through bile. However, when the liver is unable to
efficiently process bilirubin, it accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to
jaundice.
What
are the symptoms of jaundice in adults
Yellowing
of the Skin and Eyes:
One of the
hallmark signs of jaundice is the yellow discoloration of the skin and the
whites of the eyes (sclera). This occurs due to the deposition of bilirubin in
these tissues.
Dark
Urine:
Jaundice can
also cause changes in urine color. Dark, amber-colored urine is a common
symptom, indicating elevated levels of bilirubin excreted through urine.
Pale-colored
Stool:
The stool
may appear pale or clay-colored due to reduced bilirubin excretion into the
digestive system. Bilirubin gives stool its normal brown color, and its absence
leads to lighter-colored stools.
Fatigue
and Weakness:
Individuals
with jaundice often experience fatigue and weakness. This can be attributed to
the underlying liver dysfunction affecting overall energy metabolism.
Abdominal
Pain and Swelling:
Liver
inflammation or enlargement may cause abdominal pain and swelling. This
discomfort is often located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen.
Itchy
Skin:
Jaundice can
lead to itching, medically known as pruritus. The accumulation of bilirubin in
the skin can trigger this uncomfortable symptom.
Common
Causes of Jaundice in Adults
Liver
Diseases:
Hepatitis,
cirrhosis, and alcoholic liver disease can impair the liver's ability to
process bilirubin, leading to jaundice.
Obstruction
of Bile Ducts:
Gallstones,
tumors, or inflammation can obstruct the bile ducts, preventing the normal flow
of bile and causing jaundice.
Hemolytic
Anemia:
Conditions
that increase the breakdown of red blood cells, such as hemolytic anemia, can
overwhelm the liver's capacity to process bilirubin.
Gilbert's
Syndrome:
A benign
genetic condition, Gilbert's syndrome, can cause intermittent jaundice without
significant underlying liver damage.
Pancreatic
Disorders:
Diseases
affecting the pancreas, such as pancreatitis, can indirectly contribute to
jaundice by impacting the flow of bile.
Risk
Factors for Jaundice
Several
factors increase the risk of developing jaundice:
Alcohol
Consumption:
Excessive
alcohol consumption can contribute to liver damage, increasing the risk of
jaundice.
Viral
Infections:
Viral
hepatitis infections, particularly hepatitis B and C, can lead to acute or
chronic liver inflammation and jaundice.
Genetic
Predisposition:
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to conditions that cause jaundice, such as Gilbert's syndrome.
Obesity:
Obesity is
associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition that can
progress to cirrhosis and jaundice.
Medication
and Toxin Exposure:
Certain
medications and exposure to toxins can harm the liver and contribute to
jaundice.
Diagnosis
and Treatment
Medical
History and Physical Examination:
Healthcare
providers will assess the patient's medical history, including risk factors and
symptoms. A physical examination may reveal signs of liver or gallbladder
dysfunction.
Blood
Tests:
Blood tests,
including liver function tests and a complete blood count, help evaluate liver
function, detect inflammation, and assess bilirubin levels.
Imaging
Studies:
Imaging
studies, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs, may be performed to visualize
the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts, identifying any structural
abnormalities.
Liver
Biopsy:
In some
cases, a liver biopsy may be recommended to assess the extent of liver damage
and determine the underlying cause of jaundice.
Treatment
Approaches:
Treatment
depends on the underlying cause of jaundice. It may include addressing liver
diseases, managing gallstones, treating viral infections, or addressing any
other contributing factors.
OnlineHealthWealthCare's
Role in Jaundice Awareness
OnlineHealthWealthCare
is committed to promoting health and well-being by providing accurate
information and resources. Our platform offers educational materials, expert
advice, and tools to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their
health. By addressing jaundice symptoms in adults, we aim to contribute to
early detection and intervention, ultimately improving outcomes for those
affected by this condition.
Conclusion
Jaundice is
a visible manifestation of underlying health issues affecting the liver,
gallbladder, or pancreas. Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial for timely
diagnosis and intervention. OnlineHealthWealthCare strives to be a reliable
source of information, supporting individuals in understanding jaundice, its
causes, and available treatment options. Remember, if you or someone you know
is experiencing symptoms of jaundice, seek prompt medical attention for a
thorough evaluation and appropriate management. Knowledge is a powerful tool in
maintaining good health, and OnlineHealthWealthCare is here to guide you on
your journey to well-being.


Comments
Post a Comment